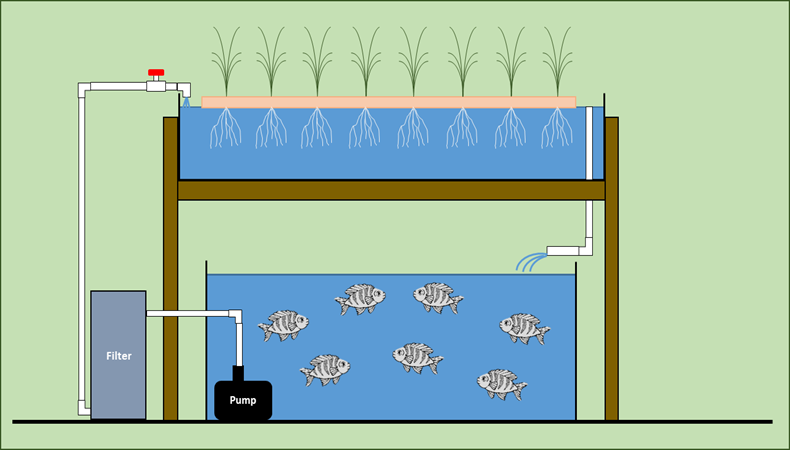
Establishing a Cost-Effective Aquaponic Garden System: A Comprehensive Guide
Aquaponics, the symbiotic cultivation of fish and plants, offers a sustainable and efficient method for food production. While commercially available systems can be expensive, a resourceful approach allows for the construction of a cost-effective aquaponic garden at home. This guide details the planning, construction, and maintenance of such a system, emphasizing budget-conscious choices while maintaining efficacy.
Phase 1: Planning and Design Considerations
Before embarking on construction, meticulous planning is crucial to ensure the success and cost-effectiveness of your aquaponic system. Several key factors must be considered:
1.1 System Size and Scale
The size of your system directly impacts its initial cost and ongoing maintenance. Beginners are advised to start small, perhaps with a media bed system using readily available materials. A larger system requires greater upfront investment in materials and a more complex design. Consider the space available, your budget, and your desired yield when determining the appropriate size.
1.2 Choosing Your Fish Species
Selecting the appropriate fish species is critical for balancing the system's nutrient cycle. Hardy, fast-growing species like tilapia or catfish are ideal for beginners due to their tolerance for fluctuating conditions. However, research the specific requirements of your chosen species regarding water temperature, oxygen levels, and waste production. Consider local regulations regarding fish farming before making a selection.
1.3 Plant Selection
Aquaponics thrives with plants exhibiting robust growth and high nutrient uptake. Leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and basil are excellent choices, alongside fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers, depending on the system's size and climate. Research plants that thrive in slightly warmer temperatures, as the water in the system will typically be a few degrees warmer than the ambient air.
1.4 System Type
Several aquaponic system types exist, each with varying levels of complexity and cost. Media bed systems are generally the easiest and most cost-effective for beginners. These systems utilize a bed filled with gravel or other inert media, where plant roots grow and bacteria colonize to process fish waste. Deep water culture (DWC) systems are simpler to construct but require more precise water level control and are less forgiving of errors. Choosing the right system type is essential for success.
Phase 2: Material Acquisition and System Construction
Cost-effectiveness hinges on sourcing materials creatively. Avoid specialized aquaponics equipment initially; repurposing readily available items is key.
2.1 Finding Low-Cost Fish Tanks
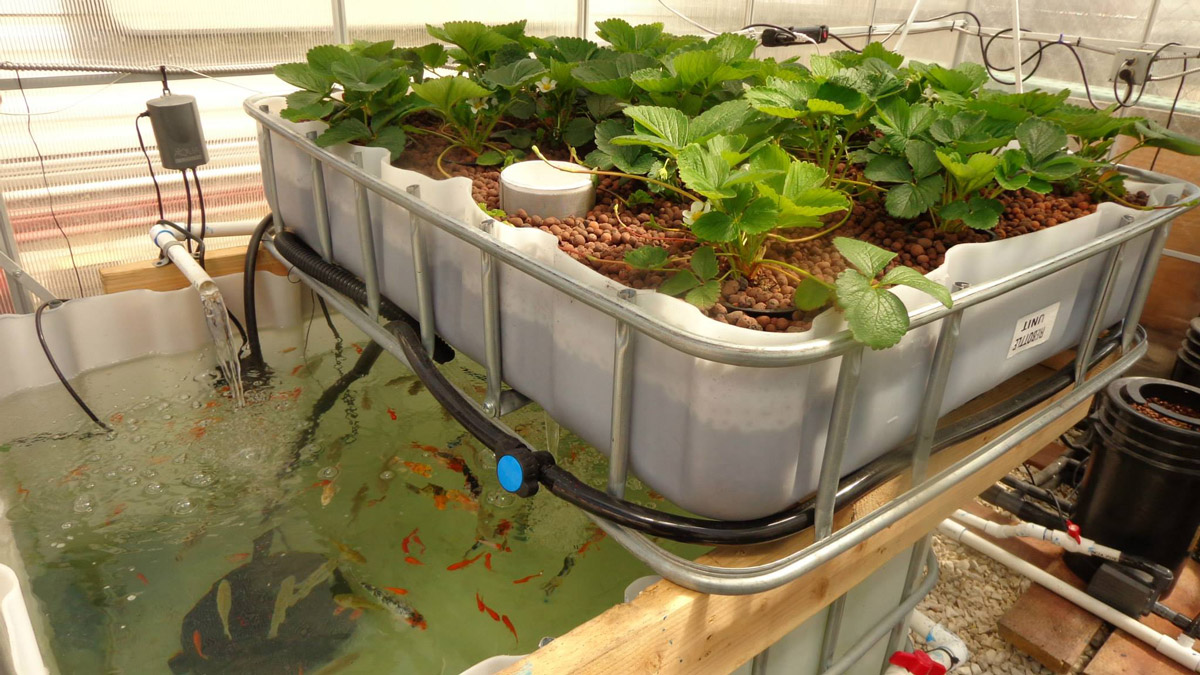
Instead of buying expensive aquaculture tanks, explore options such as large plastic storage containers, repurposed stock tanks, or even a suitably sized IBC tote (Intermediate Bulk Container). Ensure the chosen container is food-safe, leak-proof, and capable of withstanding the weight of water and fish.
2.2 Constructing the Grow Bed
For a media bed system, a simple and inexpensive grow bed can be built using readily available materials. A wooden frame lined with pond liner or a large plastic storage container can effectively serve as a grow bed. Avoid using materials that may leach harmful chemicals into the water. The media itselfâ€"gravel, clay pebbles, or lava rockâ€"can often be sourced cheaply from landscaping supply companies or even collected locally (ensure it is clean and free of contaminants).
2.3 Plumbing and Filtration
Minimize plumbing costs by using readily available PVC pipes for water circulation. A simple gravity-fed system is often sufficient for smaller setups. Advanced filtration systems can be expensive; for a starter system, a simple filter made of sponge material within the water tank is typically adequate. Prioritize a reliable and leak-free system, avoiding complex configurations which increase the risk of leaks and maintenance issues.
2.4 Lighting (if necessary)
Supplemental lighting might be required depending on the available sunlight in your location. For indoor setups, energy-efficient LED grow lights are a more cost-effective option than traditional fluorescent lights in the long run. Consider the light requirements of your chosen plant species when selecting your lighting solution.
Phase 3: System Setup and Startup
Once the system is constructed, careful setup and startup are crucial to avoid early failures.
3.1 Cycling the System
Before introducing fish, the system must undergo a "cycling" process. This involves establishing a beneficial bacterial colony that converts fish waste (ammonia) into less toxic nitrites and then nitrates, which plants can utilize. This can be done by adding a source of ammonia (such as fish food) to the system and monitoring ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels using a test kit. This crucial step can take several weeks and is essential for the long-term health of both the fish and plants.
3.2 Introducing Fish
Once the system is fully cycled, introduce a small number of fish gradually. Avoid overcrowding, which can lead to poor water quality and fish mortality. Monitor water parameters closely, ensuring appropriate temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen levels. Regularly check for any signs of disease or stress in your fish.
3.3 Planting
Plant seedlings or starts in the grow bed, ensuring that roots have ample access to the nutrient-rich water. Monitor plant growth and adjust water levels and nutrient concentrations as needed. Regular observation and adaptation are key to maintaining a healthy and productive aquaponic system.
Phase 4: Ongoing Maintenance and Monitoring
Successful aquaponics requires consistent monitoring and maintenance.
4.1 Water Quality Monitoring
Regularly test water parameters, including ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, and temperature. Maintain optimal levels for both fish and plants. Regular water changes may be necessary to maintain water quality, depending on the size of your system and stocking density.
4.2 Fish Health Monitoring
Observe fish for signs of illness or stress. Address any issues promptly. Regular feeding is essential, ensuring that fish receive adequate nutrition without overfeeding and contributing to excess waste.
4.3 Plant Health Monitoring
Monitor plant growth for signs of nutrient deficiencies or pests. Adjust nutrient levels and address pest infestations promptly to maintain optimal plant health and yield.
4.4 System Cleaning
Regular cleaning is necessary to remove debris and prevent the buildup of harmful substances. Clean filters and remove excess algae as needed. However, avoid over-cleaning, as this can disrupt the beneficial bacteria colonies crucial for the system’s function.
By carefully planning, utilizing readily available materials, and diligently monitoring your system, you can successfully establish a cost-effective and rewarding aquaponic garden. Remember that patience and persistence are key to success in this fascinating and sustainable method of food production.